|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In the intricate puzzle of human health, amino acids are the building blocks that help us maintain and optimize our well-being. Taurine, often referred to as an “amino acid,” plays a unique role in this grand scheme. This article will take you on a comprehensive journey through the world of taurine, its benefits, potential side effects, and its place in the picture of amino acids’ importance in human health.
Amino Acid Picture – The Foundation of Health
Before we dive deep into the specifics of taurine, it’s essential to understand the broader context of amino acids in the human body. Amino acids are the fundamental units that make up proteins, the cornerstone of life itself. They are responsible for a wide range of essential functions, from muscle growth and repair to the synthesis of enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters.
Amino acids are classified into two categories: essential and non-essential. Essential amino acids must be obtained from our diet because the body cannot produce them on its own. Taurine, however, is a bit of an outlier. While it is sometimes called an amino acid, it doesn’t fit neatly into either category. It is classified as a “conditionally essential” amino acid, meaning that under certain circumstances, our body may require more taurine than it can produce.
What is Taurine?
Taurine, chemically known as 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a sulfur-containing organic compound. It is naturally found in various tissues throughout the body, with higher concentrations in the brain, heart, and muscles. Unlike most amino acids, which are building blocks of proteins, taurine primarily exists in a free form, not incorporated into proteins.
Amino Acid or Not?
The debate about whether taurine should be classified as an amino acid stems from its structure and some of its functional roles. While it does have an amino group, it lacks a carboxyl group that is typical of amino acids. Additionally, taurine’s primary functions in the body often differ from those of classical amino acids.
Taurine Sources
Taurine can be obtained through dietary sources, endogenous production, and supplements.
Dietary Sources
- Meat and Fish: Animal-derived foods are the richest sources of taurine. Fish, particularly salmon and mackerel, are abundant in taurine. Meat from animals like poultry, beef, and lamb also contains reasonable amounts.
- Dairy Products: Some dairy products, such as milk and cheese, contain taurine in smaller quantities.
- Eggs: Eggs are another source of taurine, especially in the egg whites.
- Seaweed and Algae: Certain types of seaweed and algae contain taurine and are popular in some Asian cuisines.
- Supplementary Drinks: Energy drinks often contain added taurine, which contributes to their advertised benefits.
Endogenous Production
The body can synthesize taurine from other amino acids like cysteine and methionine, provided the necessary enzymes and cofactors are available.
Supplements
Taurine supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and energy drinks. People sometimes use taurine supplements to support specific health goals.
Taurine’s Health Benefits
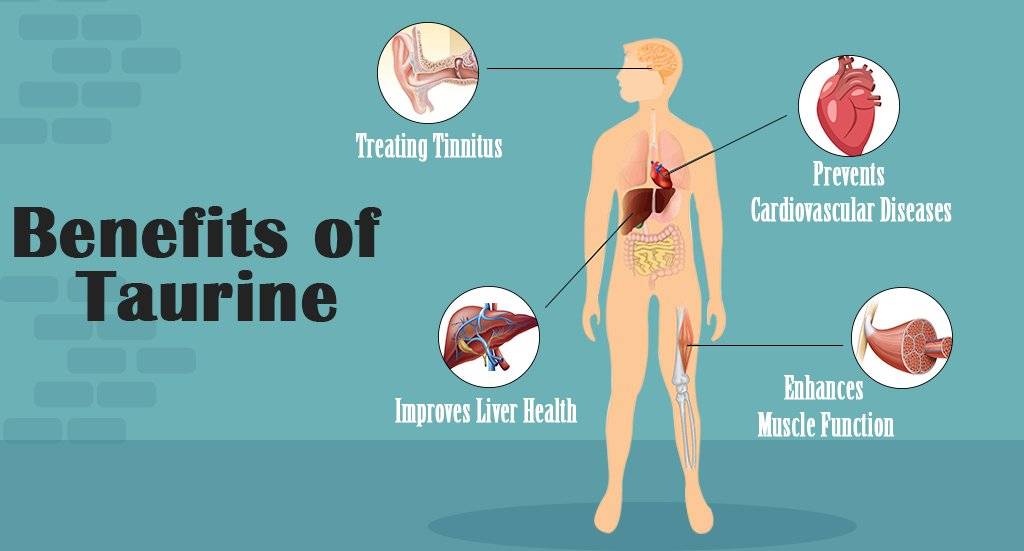
Taurine plays several crucial roles in the body, contributing to various aspects of human health. Let’s explore some of its potential benefits.
1. Cardiovascular Health
Taurine has been associated with cardiovascular benefits, including:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Some studies suggest that taurine may help lower blood pressure, making it a potential ally in managing hypertension.
- Heart Function: Taurine plays a role in maintaining the normal functioning of the heart muscle, potentially reducing the risk of heart-related conditions.
2. Neurological Health
Taurine is present in high concentrations in the brain and has various neurological implications:
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: It acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter and can help in calming brain activity, potentially reducing anxiety and promoting better sleep.
- Protection Against Neurological Disorders: Some research suggests that taurine may have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
3. Muscle Function
Taurine is crucial for the muscles, with potential benefits such as:
- Muscle Recovery: It aids in muscle recovery and reducing exercise-induced muscle damage.
- Antioxidant Properties: Taurine acts as an antioxidant, which can help protect muscles from oxidative stress.
4. Antioxidant Defense
As an antioxidant, taurine helps the body combat oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic diseases and the aging process.
5. Liver Health
Taurine is essential for liver function and has been studied for its potential benefits in liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
6. Eye Health
Taurine is found in high concentrations in the retina, and it may play a role in supporting eye health and protecting against certain eye disorders.
Taurine Supplements
Given its potential benefits, taurine supplements have gained popularity. These supplements are available in various forms, but it’s essential to use them with caution.
Dosage
The appropriate dosage of taurine can vary based on age, health condition, and specific goals. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
Side Effects
Taurine is generally considered safe when taken at recommended dosages. However, excessive taurine intake can lead to some side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses of taurine may cause stomach discomfort, diarrhea, and nausea.
- Hypotension: In some cases, taurine’s blood pressure-lowering effects can lead to hypotension, causing dizziness and fainting.
- Interference with Neurotransmitters: Taurine supplements can affect the balance of other neurotransmitters, potentially causing unintended effects on mood and brain function.
Taurine in Food and Beverages
Taurine’s presence in energy drinks deserves special attention. Energy drinks often contain taurine, along with caffeine and other stimulating ingredients. While the combination can provide a temporary energy boost, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks:
- Caffeine Interaction: Taurine in energy drinks may interact with caffeine, potentially influencing its effects on the body. This interaction can vary among individuals, making it challenging to predict how a person will respond to these beverages.
- Cardiovascular Concerns: The combination of caffeine and taurine can put additional strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure. This can be especially problematic for individuals with underlying heart conditions.
Taurine Research and Future Possibilities
Research on taurine is an ongoing process, with scientists continually exploring its potential benefits and applications. Some areas of interest include:
- Mental Health: Taurine’s role in neurotransmitter regulation has prompted research into its potential for managing mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
- Exercise and Sports Performance: The impact of taurine on muscle function and exercise recovery is a topic of interest for athletes and those interested in fitness.
- Neurological Disorders: Studies continue to investigate taurine’s neuroprotective properties in the context of disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Cardiovascular Health: Further research is needed to clarify taurine’s potential in managing cardiovascular conditions like heart disease and hypertension.
Conclusion
Taurine, despite its classification as a “conditionally essential” amino acid, plays a pivotal role in various aspects of human health. Its presence in the body, particularly in the brain, heart, and muscles, underscores its significance. While taurine supplements can offer potential benefits, they should be used cautiously, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional.
As the scientific community continues to explore taurine’s properties and applications, it’s crucial for individuals to stay informed about the latest findings. Taurine remains an intriguing piece in the intricate amino acid picture of human health, and its full potential is yet to be completely unraveled.
In the quest for optimal health and well-being, understanding the role of taurine and other amino acids is essential. As the amino acid picture comes into sharper focus, we gain a clearer understanding of how these compounds contribute to the intricate mosaic of our overall health. Taurine, with its unique properties and potential benefits, is a valuable piece of this complex puzzle, offering hope for better health and well-being in the future.



1 Comment
I just could not depart your web site prior to suggesting that I really loved the usual info an individual supply in your visitors? Is gonna be back regularly to check up on new posts.